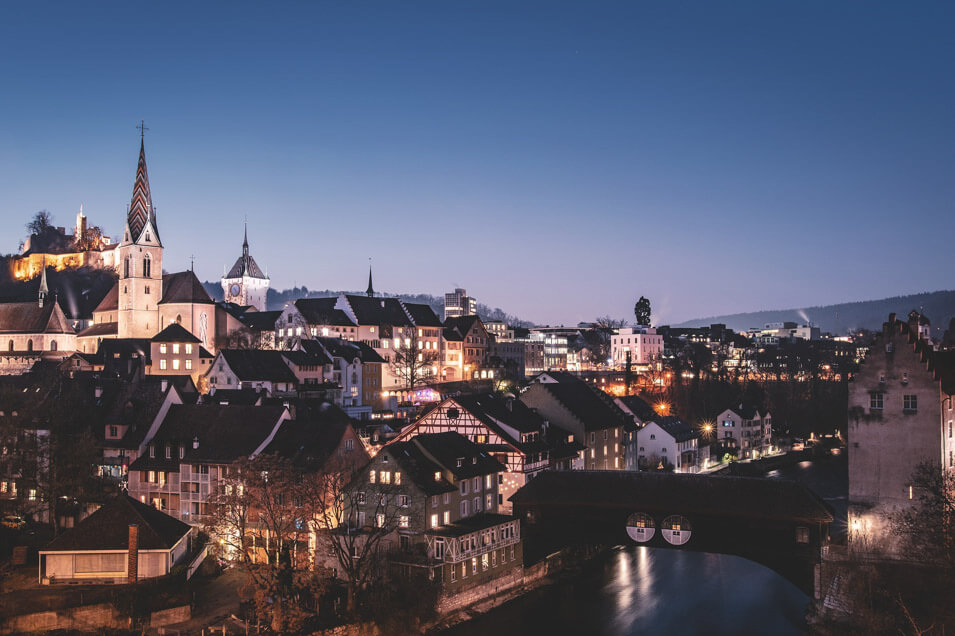
UTC:
Capital City:
Language:
Population:
Currency:
Country Code:
Domain:
+ 1
Bern
Romansh, German, French, Italian
8.79 million
Swiss Franc (CHF)
+41
.ch
Recent news
Israel-Switzerland Relations
Switzerland and Israel established their diplomatic relations in 1949. Both countries share strong and positive bilateral relations based on a solid foundation of trust, coupled with cultural, economic, scientific, and innovative collaboration. Both countries are engaged in many mutual agreements, such as the Agreement on Social Security and the Agreement on Aviation. Important to note, that in 2018, the Swiss Innovation Authority (Innosuisse) signed with the Israeli Innovation Authority a declaration of intent agreement for technological cooperation, which is a unique agreement since Switzerland chose Israel to be the first foreign country with which it signs an agreement of this type.
Israel is one of Switzerland’s most important trading partners in the Middle East and North Africa. During 2022, Switzerland exported to Israel goods and services worth $389B; on the other side, Israel’s exports to Switzerland amounted to $869M. Bilateral economic and financial relations have recently strengthened to promote trade and collaboration between Swiss and Israeli companies.
Customers who held a bank account in Switzerland are likely entitled to a fee refund as a result of a court ruling in Switzerland. For details: click here
Details of the Embassy of Israel in Switzerland
Address: Alpenstrasse 32 3000 Bern 6
Phone: +41(0)31 356 35 00
Website: Click Here
Email address: consular2@bern.mfa.gov.il
Embassy of Switzerland in Israel
Address: 228 Yarkon, Tel Aviv-Jaffa
Phone: +972 3 546 44 55
Website: Click Here
Email address: telaviv@eda.admin.ch
Bilateral agreements signed between Israel and Switzerland
- Convention for the Prevention of Double Taxation;
- Convention for Social Security – National Insurance;
- Regional Free Trade Agreement;
- Cooperation agreement between the Israel Innovation Authority and the equivalent Swiss authority (Innocuous);
- Joint membership in the WTO;
- Memorandum of understanding cooperation – financial technology;
Business Activity in Switzerland
Switzerland is a leading business destination, boasting an attractive investment environment, a highly skilled workforce, a highly developed infrastructure, and internationally renowned universities and research institutions. It also enjoys a low tax environment, stable currency, and predictable prices.
Furthermore, Switzerland is among the top 10 countries in the world by GDP per capita, with a figure of USD 92,000 in 2022. About 74% of its GDP comes from the services sector, 25% from industry, and less than 1% from agriculture. The European Union is Switzerland’s largest trading partner, supplying 67% of its imports and receiving 50% of its exports. Additionally, over 99% of Swiss companies are small and medium-sized enterprises with fewer than 250 employees.
Is important to mention that Switzerland has one of the lowest VAT rates in Europe. Most goods and services are taxed at 8.1%. A lower rate of 3.8% applies to accommodation services, and a 2.6% rate is used for everyday essentials. Moreover, Switzerland’s location provides an excellent economic environment, supported by world-class infrastructure. The country also stands out for its cultural diversity and wide range of recreational activities.
Bilateral Agreements Between Switzerland and Israel
- Double Tax Treaty
- Convention on Social Security
Convention of the Prevention of Double Taxation
The agreement between the Government of Israel and Switzerland regarding the avoidance of double taxation was signed on July 1, 2003, and entered into force on December 31, 2001.
To read the agreement in English click here.
Convention on Social Security
Israel and Switzerland signed in 1984 the treaty regarding social insurance and entered into force in 1985. The purpose of the treaty is to prevent a situation of duplication of social security between the two countries or a lack of insurance.
To read the agreement in English click here.
Applicability of the MLI
Both Switzerland and Israel have signed the “Multilateral Convention to Implement Tax Treaty-Related Measures to Prevent Base Erosion and Profit Shifting” (MLI). Israel signed the agreement on June 7, 2017, and ratified it on September 13, 2018. Also, Switzerland signed the MLI on June 7, 2017, and ratified it on August 29, 2019.
Residency for Tax Purposes in Switzerland
Residence of an Individual
A person is considered a tax resident in Switzerland if:
- They intend to permanently live there, with their main place of interest in Switzerland, and are registered with local authorities, or
- They stay in Switzerland for at least 30 consecutive days to work, or
- They stay in Switzerland for at least 90 consecutive days without working.
To read about how an individual is considered a resident of Israel, click here.
Residency of a Company
A company is considered a resident of Switzerland if its registered office is located there. Residency also depends on the place of effective management, which is where daily operations are directed or important management decisions are made.
To learn about how a company is considered a resident of Israel, click here.
The Tax System in Switzerland
The Switzerland tax authority is called the Federal Tax Administration.
The tax system in Switzerland is based on a three-layer tax system:
- Federal Tax
- Canton Tax (cantonal tax)
- Municipal Tax
Income Taxation: 21.6% – 46.2% (including federal, canton and municipal taxes)
Taxation of Companies: 8.5% – 21% (including federal, canton and municipal taxes)
VAT: 8.1%
Capital Gains Tax: 11.9% and 21.0%
Withholding Tax
Switzerland’s Internal tax rate | Israel’s internal tax rate | Treaty Withholding Tax | |
Personal Income Tax (Tax Brackets) | Federal: From 0 to 11.50 % Cantonal and municipal – depends on the canton Total rate (including federal, canton, and municipal taxes) – 21.6% – 46.2% | Up to 50% | |
Corporate Income Tax | Federal: 8.5% Cantonal and communal taxes: 11.9% and 21.0% | 23% | |
Capital Gains Tax | 11.9% and 21.0% | 25% – 30% (with an additional surtax of 3% applied to high earners) | |
Branch Tax | Federal: 8.5% Cantonal and communal taxes: 11.9% and 21.0% | 23% | |
Withholding tax (Non-resident) Dividends | 35% | 25% or 30% | 10 % |
Interest | 35% | 15%/25%/23% | 10% |
Royalties | 0% | 23% – 40% | 0 % |
VAT | 8.1% | 18% |
Inheritance Tax and Estate Tax in Switzerland
Inheritance tax in Switzerland is based on the value of the inherited assets and the kindship to the deceased. Most cantons do not tax gifts of personal belongings or household items.
The tax rate typically depends on:
- The value of the inheritance
- The relationship between the heir and the deceased
Furthermore, in Switzerland Spouses, registered partners, and direct descendants (children and grandchildren) are usually exempt from the tax. Stepchildren and foster children are also exempt, but only in cantons where they are treated the same as biological children.
Relocation to Switzerland
Switzerland is recognized as the most competitive business center globally, offering a range of compelling advantages for businesses. Driven by the country’s focus on innovation and technology, a free market economy, political stability, international connectivity, exceptional education, and health care systems, excellent infrastructure facilities along had sound lifestyle and quality living conditions among high tax favorable environment certainly make Switzerland an attractive location for business.
Switzerland’s federal tax system serves as an effective model, with taxes being established and collected at the federal, cantonal, and municipal levels. The presence of domestic tax competition helps maintain very low tax rates. The most appealing cantons in terms of taxes are internationally recognized leaders for both corporate taxes and taxes on highly skilled workers.
Key sectors that have drawn significant investments in Switzerland include information technology, precision engineering, scientific instruments, pharmaceuticals, medical technology, and machinery. The country is home to many startups. In August 2021, a new “blockchain act” was implemented, which is expected to enhance Switzerland’s already strong ecosystem for blockchain and distributed ledger technology companies.
Real Estate Taxation in Switzerland
In all Swiss cantons, upon the purchase of a house or apartment, the law requires one to pay either a property transfer tax or a fee for the transfer of ownership or land registry entry. This is charged when the property changes owners and usually amounts to 1%-3% of the purchase price. Cantons that charge a fee use it to cover administrative costs.
Citizens who own homes must pay income tax on the “imputed rental value”, which is about 60%-70% of the rent that would be charged if rented out. This means homeowners pay extra taxes. However, mortgage interest and maintenance costs can be deducted from the income through the tax return mechanism.
For citizens who own residential property, more than half of the cantons require a property tax. The tax is about 0.01% to 0.3% of the property’s estimated value. The owners or co-owners listed in the land register are responsible for paying it.
Transfer of Funds from Israel to Switzerland
According to section 170(a) of the Israeli Income Tax Ordinance, all payments transferred to non-Israeli residents are subject to a 25% withholding tax. However, this tax can be reduced or even waived if certain conditions are met. Our firm handles withholding tax matters with the Israeli Tax Authority.
As mentioned above, the countries have signed a tax treaty, that allows taxpayers to submit a 2513/2 form – Statement regarding a payment to a foreign resident that is exempt from withholding tax, to potentially transfer the payments without paying the withholding tax.
In addition to assisting with withholding tax matters, our firm also helps with other issues related to transferring funds abroad. This includes providing an accountant’s approval regarding the payment of taxes, reviewing additional actions required under the CRS standard, and more.
Moreover, banks often raise many difficulties and charge high fees for converting shekels into other currencies. Therefore, consulting with a specialist before transferring the funds is highly recommended, click here to contact us.
For more information on money transfers abroad, click here.
Types of Business Entities in Switzerland
Sole Proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is best suited for business activities closely tied to the owner. Setting up a sole proprietorship is very straightforward, allowing it to start operating quickly with minimal start-up costs. In theory, the only requirement is to register in the trade register. There’s no need for a minimum capital investment, and profits can be avoided from double taxation.
Limited Company
A limited company may be established by one or more natural or legal persons. Its share capital according to the statutes shall be at least CHF 100,000. In that respect, share capital does not need to be paid in cash; equity can also be contributed in kind, such as in the form of property or equipment.
Limited Liability Company
A limited liability company is a commercial company with its own legal identity. It requires a relatively low start-up capital. Each shareholder must hold at least one share of the company’s capital. To transfer shares, a written agreement between the involved parties is sufficient; an official deed is no longer required. A minimum share capital of CHF 20,000 must be raised.
Simple Partnership
No formal proceedings are required to establish a simple partnership. However, the elaboration of a contract is recommended. Information such as the administration of the partnership, liabilities, each partner’s contribution, profit, and loss-sharing percentage should be included. Normally, simple partnerships are established for only a limited duration of time. For instance, a construction consortium may be established for a building project alone and then dissolved upon completion of the project.
Associations
To form an association, at least two individuals or legal entities are required, with no need for starting capital. The association is established during an organizational meeting where its members approve the articles and appoint the board and auditor. The required governing bodies are the general assembly and an association board, which must have at least one member.
Incentive Laws in Switzerland
Swiss companies can reduce corporate income tax on earnings resulting from qualifying patents with the patent box system, available at the cantonal and communal level in Switzerland effective 1 January 2020. That depends on the applicable canton, up to 90% of income on the patent will be exempt from corporate income tax based on eligible research and development expenses incurred in Switzerland.
There are also competitive corporate income tax rates in the various Swiss cantons with an overall rate (federal, cantonal, and communal) from 11.9% to 21%, depending on location.
Switzerland Double Tax Treaties
Canada | Germany | Kosovo | New Zealand | Singapore | United Kingdom | |
Algeria | Chile | Ghana | Kuwait | North Macedonia | Slovakia | Uruguay |
Antigua (s.UK) | China | Greece | Kyrgyzstan | Norway | Slovenia | USA |
Argentina | Colombia | Grenada (s.UK) | Latvia | Oman | South Africa | Uzbekistan |
Armenia | Croatia | Hong Kong | Liechtenstein | Pakistan | South Korea | Venezuela |
Australia | Cyprus | Hungary | Lithuania | Peru | Spain | Vietnam |
Austria | Czech Republic | Iceland | Luxembourg | Philippines | Sri Lanka | |
Azerbaijan | Denmark | India | Malawi (s.UK) | Poland | Sweden | |
Bahrain | Dominica (s.UK) | Indonesia | Malaysia | Portugal | Taiwan | |
Bangladesh | Ecuador | Iran | Malta | Tajikistan | ||
Barbados (s.UK) | Egypt | Ireland | Mexico | Romania | Thailand | |
Belarus | Estonia | Israel | Moldova | Russia | Trinidad and Tobago | |
Belgium | Faeroe Islands (s.Denmark) | Italy | Mongolia | Saint Lucia (s.UK) | Tunisia | |
Belize (s.UK) | Finland | Ivory Coast | Montenegro | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines (s.UK) | Turkey | |
Brazil | France | Jamaica | Montserrat (s.UK) | Saudi Arabia | Turkmenistan | |
British Virgin Islands (s.UK) | Gambia (s.UK) | Japan | Morocco | Serbia | Ukraine | |
Bulgaria | Georgia | Kazakhstan | Netherlands | Seychelles (s.UK) | United Arab Emirates |