The historical events of the COVID-19 pandemic have made many countries rethink essential parts of their way of life. Within the United States, the country came to a halt in the Spring of 2020 and tested the strength of its economy. With record unemployment, the government needed to respond with intense stimulus to prevent the economy from crumbling from within; if people stopped spending, the economy could have fallen apart. Consequently, the U.S. saw a spike in spending with this new stimulus that lasted throughout 2020 and the first half of 2021. Looking past the initial stimulus leaves us at the end of 2021 into the beginning of 2022. Inflation is at a 30 year high, and labor shortages within the United States threaten the flow of goods and services between consumers and their relative markets. In combination with a domestic supply chain clog, these factors have created higher wages for low-wage workers and ensured high consumer prices across the United States could lead the country to a recession.
What is inflation, how is it caused, and what can the United States government do to try and adjust the course for continued market growth and economic prosperity?
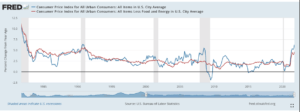
Inflation, marked as the increase in the price of goods and services, is measured by an inflation rate. The inflation rate is the rate at which the price of goods and services increases over time. The CPI can indicate the inflation rate, consumer price index. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics defines CPI,
“is a measure of the average monthly change in the price for goods and services paid by urban consumers between any two time periods…based on prices for food, clothing, shelter, and fuels; transportation fares; service fees (e.g., water and sewer service); and sales taxes. Prices are collected monthly from about 4,000 housing units and approximately 26,000 retail establishments across 87 urban areas” (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics).
Using the CPI data as an indicator for inflation across the country is common practice among economists. A rise in CPI indicates an increase in inflation across the country.
As you can see in the graph provided by the United States Bureau of Labor Statistics, CPI has significantly risen this past year and is threatening a 30 year high. Inflation is bad for the United States’ economy because raising prices can weaken the dollar’s value and discourage stable spending over a long period, an essential facet for a healthy economy. Given this information, there are some tools the United States has that can combat this impending risk.
The United States Federal Reserve is responsible for the country’s monetary policy. Monetary policy can be described as regulations enacted to control the supply of money within the country. Also known as the Fed, they can enact various strategies to try and combat impending issues such as inflation. After the influx of stimulus into the economy at the beginning of the pandemic, the Federal reserve now needs to use its tools to try and curb the rising prices.
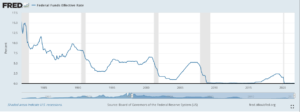
The Fed can attempt to control the rate of inflation through something known as the Federal Funds Rate. The Federal Reserve defines this as “The federal funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions trade federal funds (balances held at Federal Reserve Banks) with each other … In simpler terms, a bank with excess cash, which is often referred to as liquidity, will lend to another bank that needs to quickly raise liquidity…The effective federal funds rate is essentially determined by the market but is influenced by the Federal Reserve through open market operations to reach the federal funds rate target…” (United States Federal Reserve).
As the graph above shows, the federal funds rate has been historically low over the past 30 years. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it tries to reduce the money supply to reverse the effects of inflation. Currently, the Fed is aiming for an average of two percent inflation; however, recent CPI increases are threatening their goal and increasing pressure to raise the federal funds rate, an act which would likely lead to recession. When the fed funds rate goes up, the cost to borrow money also goes up, a significant barrier for economic growth.
With the announcement that the Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell will be nominated for a second term, confidence instability within the Fed’s policy has increased. However, Powell might need to consider policy shifts in the short term to curb further inflation. The Federal Reserve was designed as a politically independent body; its actions are not subject to other governmental influences. It is important that over the next few months that the Federal Reserve keeps an eye on inflation and potentially raises the federal funds rate. Failure to act appropriately can have detrimental consequences for the United States and the global economy. Additionally, Powell is said to have started investigating the potential of a United States digital currency; the development and research are likely to continue in his second term.
At Nimrod Yaron & Co., we serve as a professional resource for individuals and companies invested in the global marketplace. We are specifically assisting with intelligent tax planning. Contact us today to learn about all of the services we offer.